SEO Basics: A Complete Beginners Guide

Ah, Search Engine Optimization. A gold mine for some, an intimidating buzzword for others.
However, no matter if you’re the owner of a newly-launched website online, or a digital marketer who manages websites for your client, SEO will always and continuously be part of your to-do list.
What is SEO and Why is it Important for my Website?

In essence, the exact meaning of SEO is evident in the words that its acronym represents: Optimizing your website’s pages for Search Engines to find it easily.
Whenever you open your browser to start looking up stuff, search engines don’t just randomly pick from quadrillions of websites to give you what you are looking for.
It uses a complex formula, called an algorithm to produce a list of search results that would best fit the words you input on their search bar.
There’s a catch, however: search engines will produce anywhere from hundreds of thousands to billions of results depending on how broad the search term is.
This means that even if your website’s pages become recognized by the algorithm as relevant to the search query, there’s a huge chance you’ll get lost in the numerous pages of search results that a search engine will produce - and users rarely look at the second page of their search results.
As they are more likely to use a different search query than go to the second page.
This is where SEO comes into play.
It is a process that, when followed correctly, will allow you to place your web pages in front of your customers when they search using keywords that are relevant to the products or services you provide.
Typically, paid advertising is a minority compared to the amount of organic traffic a search engine can bring to your website.
While paid ads cover more of the digital real estate you see on your screen, the majority of the clicks go to the organic search results. Also, these results are more trusted by internet-savvy searchers.
The Main Goal of SEO is to give you the most desirable outcome you could ask for at the top of your marketing funnel: Placing your products or services in front of your customers when they need it.
This gives you non-intrusive and non-interruptive awareness for your brand since search queries are done intentionally by your potential customers.
Now, there are over 300 search engines that exist globally. In your lifetime, you may have come upon Yahoo, Bing, and AOL among others. However, you will find that digital marketers mostly focus all their efforts whether it be paid or organic, on just one: Google. What gives?
Why Focus on Google?
The answer is simple: Google owns more than 90% of the total market share for search engines
This means 90% of the online population uses Google as their search engine, whether it be on desktop or mobile. It is then safe to say that 90% of the customers you are trying to reach online are using Google.
With that said, let’s look at our playing field.
The Google SERP Real Estate
Search engine results pages (or SERPs) are what search engines return to a user, when they enter their query in the search bar.
How Do Search Engine Results Pages Work

Each SERP delivered to a searcher contains unique results. This means your web pages will never appear twice on a single SERP.
All search engines on the web personalize their SERP based on a spectrum of factors, to go beyond just their search terms.
These factors typically include the searcher’s physical location, web browser history, and social settings. Any two SERP pages may appear to have the same results, but will also feature key differences in them. As each user is unique in a search engine’s perspective.
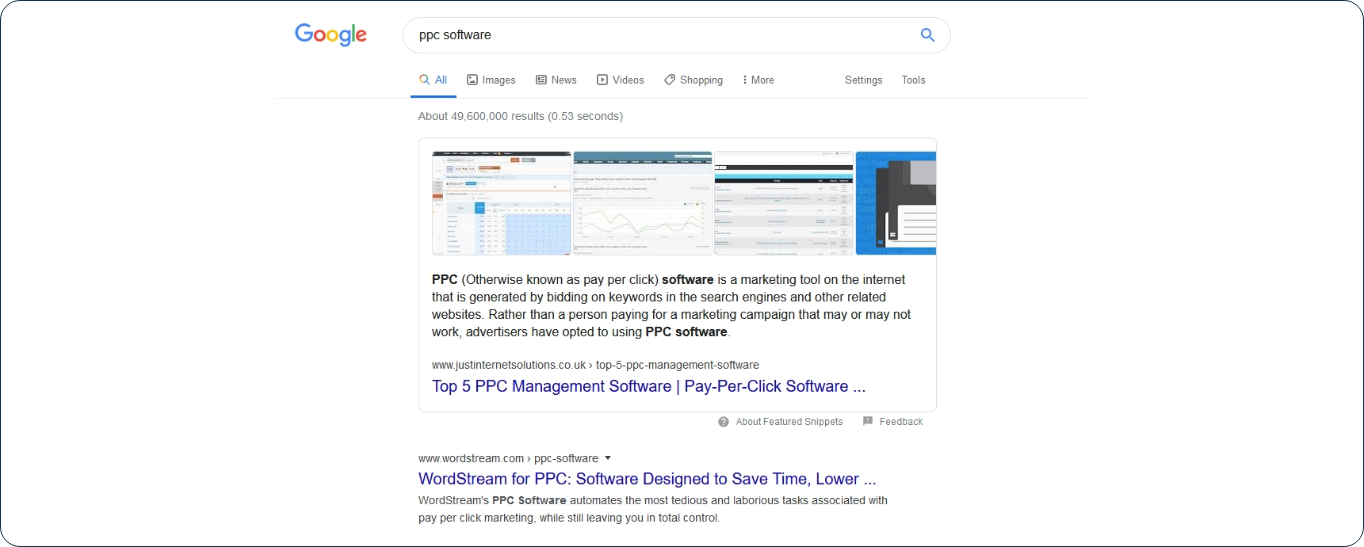
SERPs from the web’s leading search engines, such as Google and Bing, constantly change in appearance and features.
Search engines also go to great lengths to offer a more educative, helpful, and intuitive experience to their searchers worldwide.
Combined with new and emerging technologies in the digital space to update them based on newly identified needs from their customers, the SERPs of today are hardly recognizable from yesterday’s SERPs.
However, SERP has two major parts that will never, ever change: Organic Results and Paid Results.
Organic results
![]()
Organic search results are the “meat and potatoes” of SERPs. These are the natural and closest match to a keyword, or a set of keywords, from a search done by a user.
Organic results appear after Google’s search algorithms have finished evaluating, sorting, and ranking content from their huge database of website pages.
Search algorithms use over 200 ranking factors as the basis of the results they deliver to a specific user.
Knowledge of these factors are considered proprietary and kept under lock and key by Google to protect it from being exploited.
A typical SERP first page will usually hold around ten organic results. All website owners and digital marketers aim to rank their web pages here.
Landing on the second, third, or succeeding pages down the line means significantly less online traffic for their website. As I mentioned earlier, it is more probable for your customers to try a different search query in order to gain a different set of results than go to the second page.
Paid results A.K.A. Google ads
![]()
Google’s SERP also displays paid search listings or results that typically surround the organic listings. These simple text-based ads appear at the top, at the side, and at the bottom of organic results.
You can identify them by the green “Ad” box that indicates that they’re paid ads from Google.
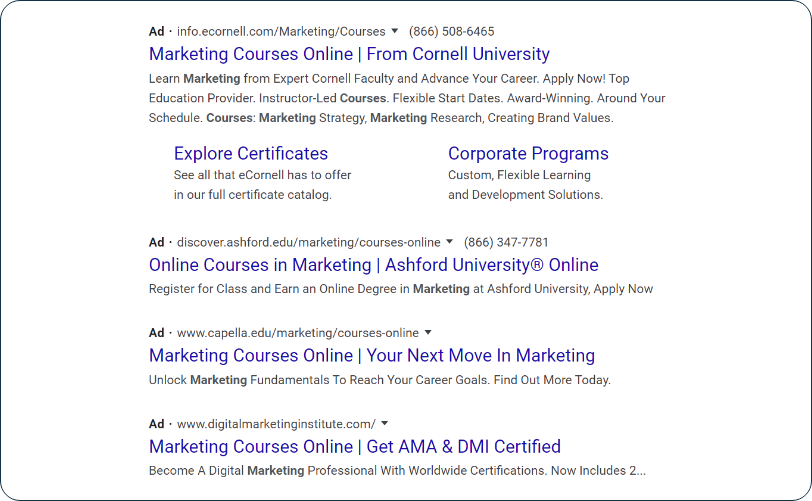

To Ads or Not to Ads
In the first part of this article, we mentioned how powerful organic results are when it comes to driving traffic to your website. The existence of Google Ads is one of the evidence that supports this claim.
Kinda counter-intuitive, huh? Ads are supposed to have more influence on your search traffic since it's a premium service that you pay for.
That is not the case in Google’s SERP space. As most often the not, you will see websites who have very robust competitors vying for their focus keywords resort to using paid ads in the hope to overtake them.
It’s not all doom and gloom though.
PRO TIP:
Running ads is not supposed to be something you continuously do for your business, unless you’re getting a good, measurable return on ad spend.
You can run ads with the aim of making your customers aware of your brand. You can also run ads for the sake of promoting your products or services during seasons when they are most needed.
The key to both points: Gaining your customers’ awareness. Which happens to be the main goal of SEO as well.
Once your customers are aware of your brand, and you’ve had enough visitors on your website for you to nurture and engage with, then you can turn off your ads.
You can also run ads while you’re in the process of optimizing it and delegate the task of driving visits to your site to a different source of traffic. Once you’re done with optimization, you can then go back on relying on organic search.
These are but some of the few most effective strategies that webmasters and marketers use to jumpstart a newly-launched website, or increase the performance of an existing one.
But wait, how do you measure your website’s success, though? How would you know if you’re doing good, or if you need to double your efforts for your website?
Let’s discuss the metrics that will help you determine how your website is performing.
The Website Performance Metrics that Matter in SEO
As an online business owner, or a budding digital marketer handling SEO for your clients, you will find yourself looking at your website analytics a lot.
First time visitors of website analytics platforms may find themselves intimidated by the sheer amount of information that is being presented to them.
However, while all the data being measured by these platforms are indeed relevant to your website, some are still more essential than the rest.
Here are the four most important metrics that you should observe:
Impressions

What It Is
An impression is simply a view. It’s when a webpage is listed in the Search Engine Results Page (SERP) . When a user inputs a specific phrase in the search bar and the search engine shows your webpage or your link URL in the SERP, it is counted as one impression.
The number of times your webpage shows in the SERPs is the number of impressions it records. So, every time your link URL appears in the search results, regardless of the page or position it is in, it records an impression.
What Google’s Algorithm is Trying To Tell You
“I found your web page relevant to the question being asked by our users. Hence, I included it as one of the search results.I’m not sure how relevant, though. Let’s let them decide on that.”

Clicks
In comparison to an impression, a click happens when you’re able to satisfy the intent or the needs of a searcher.
Whereas an impression takes place when you’re able to meet Google’s ranking algorithm standard to show up for a particular keyword search. A click is when the search engine results page shows up and a user clicks on your link URL from the SERP.
This is the action that sends a user from the results page to your webpage.
What Google’s Algorithm is Trying To Tell You
“I showed your web page as a relevant result to the search queries. The users clicked the link to your result. To me, that means they found it relevant too.
I’ll raise the ranking of your web page so the users searching for answers that you provide can have an easier time accessing it.”
Click Through Rate (CTR)

Click Through Rate shows the percentile relationship between your website’s impressions and clicks. To compute for it, divide your clicks over your impressions.
Due to the percentile nature of this metric, it is a good indicator basis for you to answer the question: “Of all the users who saw my page in SERP, how many percent chose to visit my website?
It is worth noting though, that not all clicks translates to web visits. There’s a different metric in your web analytics that keeps track of that. However, CTR still provides you with insights on how your potential customers perceive your web page on their SERP.
One factor that CTR accurately provides insights on is how effective your Meta Tags are. We will be discussing all about this valuable representation of your web pages in SERP further down this article.
What Google’s Algorithm is Trying To Tell You
“I showed your web pages to [X amount] of users and [X amount] clicked on it. Based on this I can gauge whether the way your web pages are represented on SERP is relevant or not. Of course, this also affects what your rank will be.”

Average Position
Average position, like impressions, is another metric that’s thoroughly based upon Google’s review of your website.
This shows you what your web pages’ rank has been historically. It also gives you insights on how relevant your efforts have been in optimizing your pages.
Average position is the metric that most marketers look upon as the main indicator of website performance due to how essential your rank on SERP is to your CTR.
According to research made by Backlinko from search console data from ClickFlow:
The average CTR for the #1 result in Google’s organic search results has an average figure of 31.7%
The second position can typically get 24.71% CTR
Position 3 has an average CTR of 18.66%
The 4th position enjoys an average CTR of 13.6%
Positions 5 through 7, respectively gets: 9.51%, 6.23%, and 4.15%
The bottom 3 positions have very similar CTR rates that fall below 3%.
This means that if your homepage for example is relevant enough to be in Google’s Rank 1 and you get 10000 monthly impressions for it, you are logically entitled to get 3000 to 3100 monthly clicks which would then translate to your website visitors.
And that’s just for one query. Your website is probably ranking for a hundred, if not a thousand queries.
This is why moving the needle even a tiny bit for your average position is already considered significant for your website.
A word of warning though, you may find that you have several keywords you are ranking for that puts you at the top spot of SERP. This is why it is worth checking how much impressions and clicks you are gaining from that keyword.
What Google’s Algorithm is Trying To Tell You
“It’s not about what rank you’re, it’s about the amount of clicks you’re racking up from being in that position”
Okay now that we got your website’s performance covered, and before we jump in to how we’re gonna optimize your website on-page and off-page, let’s look some SEO do’s and don'ts.
And these guidelines are divided into three ‘hats’ that you’ve probably heard of before.
White Hat vs. Black Hat vs. Gray Hat - Which One Do I Put On?
White Hat SEO: The Ethical Way to Do It

White hat SEO complies with a Search Engine’s rules or guidelines and uses techniques that are within the best practices of SEO.
These include but are not limited to: quality content marketing, improving user experience, gaining high quality links through outreach, as well as proactive and engaging interaction with your customers through social media.
With white-hat SEO, the results take much time, planning, and a lot of effort. However, in doing SEO legitimately with white-hat techniques and best practices the results are also long term.
White hat SEO is the safest and most effective approach to climb the search results rankings.

Black Hat SEO: The Dark Side of SEO
Black hat SEO strategies are the “dark arts” of SEO and are forbidden by search engines. These black-hat SEO techniques attempt to find unnatural and illegitimate ways to get around a search engines’ guidelines in order to see quick jumps in search ranking improvement.
The methods used are unethical because they violate search engine guidelines. The most common tactics are keyword stuffing, paid links, duplicate content, and cloaking.
To define these tactics mentioned, keyword stuffing is the act of putting keywords that you want to rank for in many areas in a page in an attempt to sway search engines to give you better visibility for those keywords.
Paid links are when someone buys the right to place a link into a website to produce a sense of authority for his pages.
These methods result in boosts to page rankings but they only last for a short period of time. Search engines like Google are now able to identify such tactics.
The result? They penalize a website and even worse, it can even get blacklisted by search engines.
Gray Hat: A Workaround, not the Middle Ground

Gray hat SEO refers to the methods that are being used to rank pages that are not defined by the search engine’s guidelines but does not go against it as well.
While it can be considered neutral ground between white hat and black since the risk of getting penalized is still present. The strategies include recycling old content and soliciting guest posts.
The results can be positive if done the right way. One of the best examples of Gray Hat SEO is doing research and data gathering using Black Hat methods and then implementing them using White Hat techniques.
It is worth stating again that these methods still pose some risks to your website. So best to tread lightly when utilizing them.
Conclusion:
Search engine algorithms and SEO guidelines are ever-changing with updates and constant small changes. It is in your best interest to always stay in the algorithm’s ‘Good Side’.
That being said, White hat SEO should always be the go-to strategy you can utilize. It will take a while as well as a lot of hard work before you start seeing results, but it’s definitely worth it.
Ranking high in SERP is hard enough without having to worry about the risks of penalty from search engines.
And now that you’re familiar with key SEO concepts and terminologies, let’s begin doing hands-on work with your website.
You can start getting key benefits, like generating more traffic to your website from search engines, and getting better rates of conversion from that traffic, all these from practicing SEO the right way.
Begin by Creating Relevant Content for Your Website
The Backbone of SEO: Keywords


Doing Keyword research
The goal of keyword research is to determine which keywords or phrases your prospective customers are using in the search engines that are relevant to the products or services that you provide.
It also gives you the intent of how people who need your products and services are searching online.
For one, it allows you to develop content specifically around what your target audience wants and needs.
Second, keyword research allows you to identify which keywords or keyphrases you need to target to obtain a market-share of people or searchers looking for those keywords in a given period of time.
For Example: If your business offers Gardening Services, your prospective customers won’t be using “Gardening” or “Gardening Services” to search.
They will be using search phrases like: “Affordable Gardening Services”, “Gardening Services Near Me”, or “Best Gardening Services in [Location]”.
From the results of your Keyword research, you can then determine which ones to target and focus on when creating content for relevant pages on your website. Which in turn, will be seen as relevant by the search engine’s algorithm as well as the user who is searching for it.
What is important to note about keywords is that a website, as a whole, doesn’t rank for keywords. It is the individual website’s pages that do. Single pages rank for keywords, not whole websites.
This means for every search term you want to rank for, a dedicated page on your website should exist for it.
Optimize a page by adding genuinely informative content that educates, entertains, or intrigues your target audience based on a keyword that you want to rank for.
Beating your Competition: Long tail keywords
Long-tail keywords are three to four keyword phrases that are more specific and intentionally relevant to the product or service that you are offering.
These extensively specified searches convert more customers compared to generic or broad searches (often known as “head terms”).
People who search using generic keywords are usually just browsing or researching before they buy.
However, people who search using long-tail (more specific) keyphrases are believably decided to buy something closely-relevant to their long-tail search.
A long-tail keyword identifies a searcher’s buying intent, and it is logical to deduce from their long-tail keywords an increased likelihood that they’re wanting or needing to purchase something in-conjunction with their long-tail searches.
Here are some examples of Long Tail Keywords:
Product or Service being Provided:
Veterinary Services
Main Keyword:
Pet Care
Long Tail Keywords:
Affordable pet care services
In-house pet care services
Pet care near me
Pet care clinic near me
In essence, multi-word or long-tail keywords are easier to rank for as these keywords usually have much lower competition in search engine page results and they also have far less search traffic compared with generic terms, or head-keywords.
Additionally, pages that already rank very well for head-keywords tend to already have a lot of well-placed backlinks from other relevant websites.
And if you’re just starting to develop and optimize your content it is likely that you have little to no backlinks that link back to your page.
So chances of out-ranking other competitor pages that rank well for head-keywords are very slim.
Beginner-friendly keyword research tools
Here are a bunch of note-worthy keyword research tools that will set you up for success in your SEO journey.
Is a keyword research tool made by Google for planning Paid Ads inside their search-ads platform called Google Ads. It is very easy to use as you would only need to enter your product or service keyword into the search box and it will show you the most relevant results.
It not only shows keyword suggestions, it also shows you the monthly average searches as well as how that keyword trended in the past month.
In addition, it also shows mobile search volume in relation to total search volume. Very useful for businesses who also rely on mobile platforms for both awareness and conversions.
As mentioned above, Google Keyword Planner exists inside the Google Ads Console. This doesn’t mean that you can gain access to the Keyword Planner only if you’re running Google Ads.
All you have to do is create a Google Ads account for your website - which will be very useful in the future if you decide you want to run PPC campaigns.
PRO TIP:
Google Keyword Planner also provides insights on PPC Bid amounts. This information is not only useful for those running ads, it is also beneficial for organic SEO.
High bid costs means that a lot of advertisers are running ads on the same keywords. This means that even if you rank favorably as the Top 1-5 results in SERP, there’s a very high chance that Google Ads will exist above your website in the ranking.
While Google’s in-house tools like the Keyword Planner and Google Trends discussed previously provide accurate results, they mainly focus on one aspect of the SEO process. Hence the need for all-in-one or what I like to call “Swiss Army Knife” SEO Tools.
These tools provide insights on several fronts: Keyword analysis and suggestions, Domain checkers, and Website Audits among other things.
Moz Keyword Explorer is one of the best Swiss Army Knife SEO Tools available online. It provides you with insights on search volume, organic difficulty, and average Cost Per Click.
However, there are three factors that make it stand out among other SEO Tools: Context based Keyword Suggestions, Organic CTR, and Priority.
Context based Keyword Suggestions provide you with out of the box suggestions for your target keyword.
Let’s say your focus keyword is ‘weight loss’. Normal keyword suggestions (even Google’s) would revolve around: ‘Best weight loss techniques’, ‘weight loss exercises’, and ‘weight loss diet’.
In MOZ, see keyword suggestions like: ‘How to burn fat quickly’, ‘best cardiovascular exercisesyou’ll ’, or even ‘how to do burpees’.
Organic CTR shows you an estimate of how much clicks you could be getting if you target a certain keyword.
Priority takes several metrics into consideration like search volume, clicks, CTR, and average position to tell you which keywords you should prioritize first in content creation.
MOZ Keyword Explorer is Free to access for everyone. If you are a small business owner or manager taking care of a single website, then the features that come along with the free access would be sufficient for your needs.
However if you’re scaling up your business or if you’re serving the needs of multiple clients, then you would be needing the additional features that comes with upgrading to MOZ Pro.
Now that you have data on your focus keywords -and probably long string ones as well. The next tool we will recommend to you will take that to the next level.
Google Trends is another SEO tool made by google that adds the factor of time in your data. While average search volume may show you relative keyword performance per month based on how many users are searching for it, these numbers may not necessarily equate to how popular your focus keywords are at any given time. And that is where Google Trends comes in.
You may be thinking: “Okay, so this tool will show me when my focus keywords are popular during the year, or which seasons my keywords will be trending in searches.”
You’re right. But it does more than that. Google Trends allows you to do two things for your keyword research: Strengthen your website’s content and expand your content topics’ horizon.
The former is a bit of an obvious point: Knowing which of your focus keywords are popular and which are not in any given time will help you decide which to focus on and which ones need to improve.
Expanding the horizon of your content topics is how your web pages will shine. Let’s say you own an electronics store selling computer parts. Knowing which season your potential customers tend to buy new computers is one thing.
Knowing why is another. School starting in a few months? Create content that will make your products relevant to the upcoming school year. E3 happening soon? Know which video games will be the next popular thing to gamers and create content revolving around it.
There’s endless possibilities that will open up for your website content.
The best content strategy is not a one-size-fits-all plan for the articles, videos, or infographics that you will produce for your site. It is when your content fits the current trending topics for that given time or season.
If MOZ Keyword Explorer can be compared to a swiss army knife, KW Finder is a specialty tool. It does one thing and it does it best: keyword recommendations.
Before we go into features, we’d like to first discuss how intuitively user-friendly and beginner-friendly this tool is. Anyone, whether you are a beginner at SEO or a high level digital marketing expert would have an easy time navigating it’s easy to use UI.
KWFinder is one of the best tools when it comes to finding precision Keyword suggestions for your site’s content creation team.
What makes it special? Keyword opportunities. These are long-tail or question-based keywords that your competitors often fail to notice but has the potential to gain that much needed ranking for your web pages.
KWFinder does have a steep price for its premium services, though. But if you’re a business that’s looking to scale up, or an agency that caters to multiple clients? Then KWFinder is definitely a must have tool in your arsenal.
A friendly reminder, though: One of the important aspects that even SEO experts sometimes neglect is the fact that we are all following the same guidelines in terms of optimization processes. We’re mostly looking at the same tools, at the same data, and making the same analysis and conclusions. We’re all dancing to the same tune that Google is playing for us.
Being competitive in this growing SEO world in the digital space means doing something that others don’t. However, if you find that innovation is too costly or is not in your capabilities right now, then do the next best thing: Do it better. And we’ll show you how:
Targeting Search Intent

Gone were the days when content creators needed to strike the delicate balance between using robot language and making content that’s engaging for human beings.
As we have previously established, SEO’s goal is to place your product and services pages in front of your customers when they need it.
However, SEO only covers the beginning of your sales process, which is located at the top of your marketing funnel. SEO is just showing your storefront to customers who need them. The next step is having your customers recognize your storefront for what it is: The answer to what they need.
This is where Search Intent comes into play. Recent Google algorithm updates blurred the line between machine language and human language by teaching machines how humans form sentences, structure statements, and generally how humans search for an answer to their question.
To simplify: Search intent is the “Why” of your customer’s search. It goes beyond keywords and queries and defines why a user searched for something.
In other words, why did the person make this search? Do they want to learn something? Are they looking to make a purchase? Or, are they looking for a particular website?
For example, a user searched for: Top PC Games in 2016.
Does this mean he wants to know what the top games were a couple of years ago? Is he looking for a specific game that was released in 2016? Probably not.
He probably has a dated rig and the only games that could run on it smoothly were games made back in 2016.
For Google, search intent is a paramount requirement for website owners who are aiming to rank their website. Their aim is to provide their users with the most relevant results to their queries.
They even stated it on their mission statement:

Determining an individual's intent for searching a keyword in Google is important for your SEO strategy. It will tell you how to better optimize a piece of content and relate it better to keyword queries.
When you know exactly why a user is searching for that particular keyword, you'll have the ability to tailor your website's content. This will ensure that your web pages, as a result to queries, better meet a user's need for information.
How Do You Identify Search Intent?
For starters, know your customers.
Who are your customers? How old are they? Which generation do they belong under? Where do they live? What language do they use? Where do they spend their time when they’re online? Most importantly: What are they thinking about when they decide they need your product or service?
These are but a few questions that you will need to answer to establish search intent.
Then, organize the answer to these questions in Customer Personas. Once that is done, identifying how each persona is different in terms of how they search and why they put up queries in Google would be your next step.
You can now begin identifying focus keywords around each of your Customer’s Personas. Expand these keywords through research and analysis, identify long tail keywords and queries, and create content that caters to each personas’ search intent.
Sounds easy right? Well, we’ve only just begun. Now that you have your focus keywords at hand supported by search intent, it’s time to pimp your website for SEO. Our next step?

Optimizing your Website and its Pages
We mentioned earlier that relevance is very important for Google and that the algorithm must find that every aspect of your website is relevant to your customers search intent. This is the only way for your web pages to rank high in SERP.
However, SEO is not limited to content creation. Yes, content is where the most of your efforts to optimize your site will be spent. But there’s more, equally important aspects.
The process of optimizing all these aspects, including content creation, is called On-page Optimization.
Because a clean home invites more guests in.
There are actually numerous steps and processes that you would need to cover for On-page Optimization. To make it easier, let’s divide it into two main parts: Direct and Support
Direct Optimization
These are steps that revolve around your keywords and their search intent. Hence, the term Direct Optimization since these steps will directly impact your content.
Each of your website’s pages have three main parts:
Representation
This covers aspects of how your content is seen by outside sources.

Structure
How your page’s content is presented to readers, and

Body
The main chunk of your content.
Let’s look at them one by one:
Representation
The first aspect of your content’s representation is called the Metadata. Don’t be intimidated by the term, it’s parts are actually pretty straightforward.
One important thing you need to remember about the parts of Metadata is character limitations.
Exceeding the character count does not necessarily mean Google will penalize you.
However, the algorithm’s spider would only ‘read’ up to a certain number of characters before moving on.
Also, it would render your page’s title and description incomplete to the human reader. See example below:
Which, in essence is actually worse than being penalized by Google. Since it directly impacts your conversions and click through rates. You want your pages to be represented completely to your customers.
Let’s look at each part closely:
Your Meta Title.
This represents your page’s content to users in SERP.
Like any good title, this is where your focus keywords backed by search intent should be located.
The character limit for Meta Titles varies depending on Google algorithm updates. It would be best to use a SERP Preview tool to make sure your Titles are within the character limitations.
Your Meta Description.
This part of your Meta Data exists for conversions.
This is where you should put your best efforts in convincing your customers to click. Don’t worry, the high number of allowed characters for this section will make sure that you can work towards that goal.
Google’s algorithm does not necessarily take Meta Descriptions into account when scanning for SEO relevance, but the search engine does one thing that has critical impact to converting your impressions into clicks: It bold the keywords that your customer used to search on your Meta Description.
Further reinforcing the fact that this section is meant for conversions and not impressions.
Structure
If you’ve been on the internet long enough, then you probably know what a “wall of text” is and why everyone hates it. Well, now even Google’s algorithm hates them.
Google’s bots used to be completely okay with walls of text, back when they were only scanning for keywords en masse. However - and as we mentioned earlier, Google is moving their algorithm’s direction towards understanding how humans ‘read’ words, sentences, and even paragraphs.
This is where your content’s structure comes into play.
To keep this simple, let’s use a real world example: A presentable, well thought out article would be divided into sections. In each of these sections are paragraphs that focus on one thought and then transitions to the next one. Finally: each section would have a header that gives an overview of what topic the section below it tackles.
The same principle is true for Google. Following the hierarchy of headers, from H1 to H6 is very important for the algorithm, but more importantly for your customers who are consuming the content as well.
By now you may be seeing a pattern: Google’s Algorithm is moving away from just showing results or impressions, to presenting relevant content to its users.
Body of Your Content
Back in the day, there existed an SEO method that everyone was using to rank their pages easily. Content creators and copywriters used to do this at any chance they could get in order to ‘appease’ the search algorithm.
They didn’t have a name for the method before. Now we do. We call that technique Keyword Stuffing.
You’ve probably seen examples of these (and probably still see them) on old, dated websites. Keyword Stuffing is the process of placing as many keywords as possible in a page, an article, the metadata, anywhere possible for that matter.
Here’s what the results look like:
“We sell custom cigar humidors. Our custom cigar humidors are handmade. If you’re thinking of buying a custom cigar humidor, please contact our custom cigar humidor specialists at custom.cigar.humidors@example.com.”
Looks bad, right? Now imagine a whole page that has keywords stuffed on it. It’s probably a page that you wouldn’t last a minute on.
Keyword Stuffing is a thing of the past. Content creation now has a very simple rule.
Actually, it is very ironic that the part where most of your efforts for on-page optimization will be spent on has the simplest guideline: Create great content.
But how do you make great content? It’s simple, really: Stop thinking about SEO for a while and think instead about your customer.
This is where you combine your keyword research, your customer’s persona, and their search intent to create content that fulfills your websites role.
And your website’s role in your business is not to rank high in Google or any search engine for that matter. Your website exists for your customers.
Support Optimization
These are steps that you need to take in order to reinforce your Direct Optimization efforts. They are very straightforward:
Your page URLS: Keep them short and direct to the point. Your URLs should represent what your page is all about
Internal Linking: The idea behind this is very simple. If you have content on your page that supports or reinforces a context on your new article, link that statement to that page. This does three things:
●Provides your reader additional content to read upon that would strengthen the context you are linking from (Which is the main purpose of internal linking.)
●If your reader is in need of further explanation on the context, they will stay on your website instead of leaving to go to another site
●Increases the authority of your page’s articles since they are supporting and referencing each other
Alt Text for Images: Your images provide reinforcement to the ideas that you are presenting in your content. Google’s algorithm sees the same purpose in your website’s images. However, advanced as it may be, Google’s bots have no eyes. They cannot scan images. So don’t leave the images on your website with gibberish filenames. Tell them what it is, what it contains, or what it represents. You can do this through the images’ alt text.
The next aspects of On Page SEO Optimization are a bit on the advanced side, but are definitely worth looking into and applying to your website’s pages:
Schema Markup
Schema markup is a code that you install on your website to label or organize your content. It helps search engines understand your web page.
Schema is also referred to as ‘structured data’ In simple terms, it holds the hand of Google’s spiderbot and tells it where to go first on your website’s pages.
A website called Schema.org helps provide schema markup codes. Google’s Understand How Structured Data Works is also a useful read for more information on the topic and how to implement it.
You can test your schema markup after you put in place by using Google’s Structured Data Testing Tool.
Robots.txt
Robots.txt is a file used to instruct search engine bots whether they can or cannot crawl parts of a website. It follows the robots exclusion protocol (REP), a standard used by websites to regulate how web robots crawl a website.
The crawl instructions tells Google’s spiderbot whether they are allowed to perform certain actions such as indexing, categorizing, and scanning your web pages for duplicate content in the process of ‘crawling it’
Robots.txt is useful if you have orphan pages, or Landing Pages that you are looking to drive exclusive traffic to such as: opt-in opportunities or pages that exist in the middle of a sales funnel. Pages where customers driven by organic traffic would have incomplete intent, or lack of nurture that are part of the initial steps of your sales funnel.
The Sitemap File
A sitemap is a file that lists the individual pages on your website. To any visitor -whether it be a bot or a customer, your website is like a theme park. Your pages are the rides and the attractions. A sitemap is, well, a map that shows them which attraction they are actually looking for.
Having a sitemap enables search engines to crawl your website better because it tells search engines about your website’s pages and content for them to aptly crawl your website. This helps in further improving your search results and traffic.
Your sitemap is useful to both users and search engines. Users prefer an HTML sitemap, while search engines prefer an sitemap in XML format.
There are different tools that can help you create an XML sitemap for your website. After creating one, you would then need to submit your sitemap to search engines. However, when creating sitemaps, it is worth reading through the sitemap protocol to ensure you are on the right path.
Now that we have the basics of On-page Optimization covered, let’s make the process easier by giving you recommendations on tools that you could use for On-Page Optimization.
The Best Tools to help you in On-Page Optimization

SEOCrawler, from it’s name is a website crawling tool. It’s best feature: Their site auditor that allows you to:
Analyze page speed (more on this when we discuss Technical SEO)
Find duplicate meta titles and descriptions
Spot duplicate content on your website
Identify broken links that exist on your pages
From an organic ranking perspective, it’s best to have unique, original content on your site.
Now, if you’re the one creating content for your site then you can at least be sure of the integrity of the articles you are publishing. However, if you’re a site owner who hires freelance content writers to make your articles, then there’s a risk that Google may find duplicate content on your site.
Copyscape makes sure that you don’t. Here’s what it will do for you:
It checks your site for duplicate content that exists on other sites
It also shows you if other sites are copying your content so you can file a plagiarism claim
Copysentry then provides you with advanced protection by scanning the web daily or weekly and alerting you by email

Similar to MOZ, Ahrefs is another “Swiss Army Knife” that allows you to do different things in one platform. However, what earned Ahrefs a special mention in our article today are the unique features that it brings to the table when it comes to On-page Optimization.
Let’s take a look:
Content Gap Tool - analyzes the keywords you use vs the ones your competitors use and provides you with unique opportunities for targeting keywords
Content Explorer - combine Google’s Keyword Planner with Google Trends and this is what you’ll get. It gives you insights on what content to publish at any given time which would be relevant not only to the current season but also current events.
Keyword Cannibalism Tool - this is a unique feature in that it actually tells you if two or more pages on your website is competing for the same keyword. This is very useful not just for ranking your pages separately, but also expanding your site’s scope of relevance
Ahref’s Toolbar - a very useful tool for when you find yourself doing content research, or just looking for inspiration for your the next article you will be publishing. Provides you with vital SEO metrics in SERPs while you’re browsing. Only available on Google Chrome and Mozilla Firefox browsers.
Content explorer
SEO toolbar
Building Site Authority and Reputation with Offpage SEO
So far, we’ve shown you the steps you need to take to fortify your website through on-page SEO, it’s now time to look outwards.
Your website’s storefront looks good. Your product pages are engaging and spiffy. Now let’s get people to talk about your brand.
Off-page SEO is the process of building your site’s reputation and authority. It tells Google’s algorithm that your brand that can be trusted, and that your site’s pages are worthy of the top ranks in SERP.
The requirements of having expertise, authority, and reputation (or Google’s EAT Guidelines) becomes more critical if your website, or your business, is classified as YMYL.
YMYL stands for Your Money or Your Life. These are brands whose products or services have a direct impact on human life or lifestyle. Websites that create medical-related articles, provide financial or investment advice, or online stores that sell workplace safety equipment, are just a couple of examples of a YMYL site.
If your business is classified as YMYL, then you would need to increase your brand’s reputation and trustworthiness twofold. Social proof like testimonials, positive reviews, or people talking about you in Social Media; Entities that supports your brand’s reputation such as awards you have received, or certifications you have earned, will help in increasing your brand’s reputation.
Here are additional systematic ways that you can do to build your website’s online reputation:
How Backlinks Work and Using Link Building to Get More of Them

Backlinks are simply one website linking to another.
They’re essentially a vote of trust from one page to another.
Also referred to as “incoming links,” the more links you have pointing to your pages, the better your site’s ranking and search visibility is going to be.
Link building is the process of getting links from other websites to refer to your web pages.
That statement might be very intimidating, especially to a beginner in SEO. So let’s make it less daunting:
Let’s say you are a new owner of a small store that sells high quality pet care products. You’re pretty confident that your goods are the top of the line, and you also believe that your customers will love what you’re offering them. However, you just opened your store so pretty much nobody knows you exist yet aside from those random people that pass by your shop every day.
Turns out that two blocks away from you is a trusted veterinary clinic who has a regular influx of customers. You knock at their door, introducing yourself to the owner, he invites you into his office and you have some coffee together. You tell him about your shop, he’s very familiar with the products you sell and he agrees it’s top notch. You then ask him if he could recommend your goods to his patients and he agrees.
That’s how link building goes. It is a continuous, dynamic process and nowadays, building high-quality links is the name of the game if you want to succeed online.
That said, here are several Link Building Techniques that you can implement to build out your website’s reputation and authority:
Guest posting
This is the process of writing and publishing a piece of content on someone else’s website or blog. With you being the ‘guest writer’.
The goal is to have links on your ‘guest article’ that routes whoever clicks it to your website. That’s the easy part. The next step is convincing the website or blog owner that your content is the bomb.
That’s not necessarily a hard thing to do. It just takes work and dedication. The content you create should be well thought out, of high quality, and benefits the host as well.
The last step? Knock on their door, introduce yourself, and request that they include your article in their website or blog - by sending an email.
Oh, and there are some sites and blog platforms that accept guest articles too. You’ll just have to do your research to find two or three from your niche, and you’re good to go.
One thing to note though: Never create duplicate content. Don’t submit articles that you already have on your website to other sites. And don’t submit one article to different sites as a guest post. These host sites will know, and you will lose a platform to post on.
The best way to do it? Create a “Main” article on your website that would serve as reference for multiple topics. Then create different supporting articles which you could link to your main article and submit that as guest posts. That’s a cleaner and much more efficient method.
Link outreach
Reaching out to other webmasters with the main goal of having them link to your site is known as “link outreach.”
Most people do this through a simple e-mail, Facebook message, or a tweet.
One you have a basket of sites you’d like to try to get a link on, the next step is to research who owns the site or who would be the best person to contact. It’s usually the person running the blog or website itself.
Link outreach is considered one of the safest and most effective means of building links. I’ve even heard of some SEOs getting links from major publications just with a short phone call.
Fixing broken links
Ever go to a website, click on a link and suddenly get routed to an error 404 page? That’s a broken link. And it usually happens to websites that have existed for years and have not had the time to maintain their old posts or pages.
Broken link hunting is an “I scratch your back, you scratch mine” deal.
The process is pretty straightforward: You find a website that matches your niche, you use a tool that then looks for broken links like Neil Patel’s Ubersuggest, then you create content that would replace that would match what the old content was in there.
The next step? Knock on their door by sending an email, introduce yourself, tell them that their link is broken, and offer your content as a replacement.
Here’s the key takeaway: No one likes broken links on their site. That’s bad for SEO, and also bad for user experience. However, most web owners don’t have the time to create the content that would replace the broken one (they didn’t even have time to check in the first place). And that’s where your content comes in.
Quora and Reddit
Quora and Reddit are what we call community platforms. They both function much like a forum.
These platforms have very high potential for building links, as there are millions of active users on them at any given time. Plus, links on these platforms provide an extra benefit aside from back links due to how active the community is: Organic visits to your site.
For Reddit, you can post a topic discussion or comment on an ongoing one, making sure that your website’s link is included on the post or comment.
For Quora, you can look for questions that can be answered by your product, service, or content on your website. You then include a link to your website on your response.
Easy right? That’s because there’s a catch.
I mentioned this earlier but it's worth mentioning again: Quora and Reddit are community platforms. These are sites with very heavy, invested, most of the time emotional,f engagement from its active users

Social Media
Now this one does not require that much of an explanation. Like Reddit and Quora, communities exist in Social Media. Building a page for your brand on these platforms is also beneficial for your brand.
Here’s several reasons why:
Social media posts also get crawled and indexed by search engine spiders. Try googling your exact name. You’ll probably have either your Facebook or your LinkedIn profile as the first result.
It helps build brand authority and reputation organically.
It involves real human engagement, a valuable aspect of conversions.
Which Social Media channels are still viable for 2020?
Facebook is still one of the biggest and widely used social media sites. It is a good place to get website visits, content engagement, and leads. Many users visit a brand’s Facebook page first before actually visiting their website.
Twitter is another social media platform that is very popular especially to younger generations. However, in order to reap its benefits, you must be an active user. So remember to tweet regularly, use appropriate hashtags and use headlines that captivate your audience.
Instagram is a visual social media platform. It is a great place to showcase products through images and recently, videos. Brands that are into fashion, beauty, and arts take advantage of this site to promote their products or services.
LinkedIn is a professional platform best used for connecting with businesses. If your target audience is more on the professional, white collar side, then LinkedIn is for you.
● YouTube
YouTube is also a great platform for brands that create videos and grow your brand awareness. Since videos are mostly created for entertainment, they tend to catch the attention of users which gives them the opportunity to engage with the content.
Now that you know how to build links that add reputation and authority to your site, it’s time to optimize them. Here’s how:
Off-page Optimization

Rating Links and Disavowing Bad Links
Backlinks can either be good or bad. Good backlinks help your website increase its Domain Authority (DA) and Page Authority (PA). On the same token, bad links can harm your website and cause it to lose rankings.
The good news: you can do something about these bad links. Google’s Disavow Tool is a very important online app to have in your arsenal as it would allow you to disavow bad links that are connected to your site.. Disavowing is the process of letting search engines know that you do not want them to count certain links when they are crawling your website.
It is important to note that the Disavow tool should only be used as a last resort. First and foremost, try to manually request link removal from the site owner. There is always the possibility that the owner will allow your request and remove the link.
Link popularity and Domain Popularity
Link popularity refers to the number of incoming links to a website. These backlinks are counted individually. It used to be a numbers game as search engines find link popularity a valuable factor in SEO. Now, search engines focus on domain popularity since it provides information on a backlink’s quality.
Link juice
Link juice is a term that refers to the value of a link on a web page that links to another or from one website to another. The link location affects the potential juice of a link. Contextual links on a page tend to pass more link juice.
Dofollow vs. Nofollow links
A dofollow link or a follow link is a hyperlink that will pass the SEO strength, or "PageRank" of the page to the site that it links to.
For example: a page in Wikipedia or Forbes that ranks high for a certain query has a link that directs to your website.
A nofollow link is a hyperlink that is not counted by search engines like a comment to a social media post or a forum topic. These links do not pass link juice and do not help improve Page Rank. They can still be a good source of organic traffic, but it won’t help with search engine rankings.
Now that you’ve built out your website’s authority and reputation as well as optimized your Off-page SEO. It’s time to circle back to your customers needs: An awesome User Experience.
Focusing on User Experience
Before we go into the technical side of User Experience, let’s talk about one very simple guideline: Your website needs to tell the story of your brand to your customers. And your storytelling needs to be as streamlined as possible.
That’s the main idea behind UX. Creating an awesome experience for your users.
User experience (UX) is an important element of search engine optimization. Search engines like Google now have stricter algorithms that make UX a highly valued criteria for rankings.
A concrete example of this is the RankBrain algorithm. This algorithm focuses on UX signals, defined as behavioral patterns of the users who visit your site.
Some of these signals are a website’s bounce rate or how “quickly” a visitor on your website leaves, organic click-through-rate (CTR) or how many users who saw your web pages in SERP actually go and click on your link, as well as how many pages an average user visits on your website per session.
Circling back to our earlier point, search engines take into account how happy users are when they visit your website.
UX Design Best Practices for SEO

Improve your website’s page speed or page load time. No one likes a website that takes forever to load. Recent studies show that the average human attention span is 8 seconds -shorter than a Goldfish. If your website’s homepage or your landing page does not load within that timeframe with enough time for the visitor to read your page’s header, then you’re in big trouble.
The following aspects may help you in improving page’s loading speed:
● Choosing a reliable hosting provider
● Compressing images on your website
● Taking advantage of browser caching
Make your website as responsive as you can for mobile users. Many individuals rely on their mobile phones when searching online. This is further supplemented by Google’s “Mobile First Indexing”, in which the algorithm evaluates how fast a page can load on a mobile platform before it considers desktop or laptop loading times.
Make your website’s architecture simple. In general, this means that search engines should be able to find and index your pages easily. Optimize your layout for a streamlined customer journey and have a user-friendly navigation menu. Keeping these in mind will not only satisfy the algorithm’s requirements, it will also make your website visitors pleased with your site.
It’s worth stating again: Don’t prioritize SEO. Your priority is your Customer and their journey on your website’s pages. Keep this ideal close at heart and you will also meet SEO requirements.
You are a customer too, a visitor to other websites and their pages. The factors that you don’t like and the aspects that make your visit to these websites unsatisfactory? Don’t do it.
Okay, you now know how to optimize your website on-page and off-page. How do you determine if you’re doing well? How can you measure performance?
Here are some tools that would help in benchmarking your results and provide insights on how you can improve them further:
Measuring Performance
Essential Google Tools

Google Analytics is a tool that lets you gather, collect, and analyze the data coming from your website.
It tracks your website’s performance across several metrics like sessions, users, session duration, and page views among others. It is a very powerful tool in helping you understand your audience to further improve your website and tailor it to their needs.
Google Search Console is another free service provided by Google. The main goal of the Search Console is to help you monitor and maintain your website’s performance in the search engine.
It also has functions that can help you troubleshoot some issues that affect SEO performance. The following can be monitored in Search Console:
website indexing
website crawlability
traffic data
search queries
Conclusion
SEO may seem like a daunting undertaking for website owners and online entrepreneurs. But just like any other aspects in business, knowing is half the battle.
And SEO is all about knowing what the latest trends and updates are, and how they change the game.
Google’s Algorithm undergoes updates up to 3,200 times in a year. This means several advanced guidelines and methods that work now may no longer work tomorrow. That’s how volatile SEO and Google’s Algorithm is.
What’s important is that you have the basics covered, and that your mindset is in the right direction.
And that right direction is: Put your customers first.
All the branches of Digital Marketing, whether it be PPC, SEO, Conversion Optimization, all point towards one thing: Your customers.
